
Blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI) concepts are unquestionably growing in popularity. However, both technologies differ in terms of their level of technical complexity and their wide-ranging business ramifications. Moreover, a widespread misconception is that a blockchain is decentralized and, consequently, not under any one person’s authority. But a group of core developers are still behind developing the blockchain system’s foundation. This article aims to shed light on the implementation of blockchain in AI on the one hand and the significance of AI in developing blockchain technology.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Intelligence refers to understanding concepts in unique ways. Individual intelligence and collective intelligence are the two types of intelligence in nature. As the name suggests, artificial intelligence is intelligence that developers have created artificially in a way that can evolve automatically. To date, numerous artificial intelligence techniques, such as neural networks, support vector machines, and fuzzy logic, have emerged. engineers has successfully employed these methods in robotics, economic modelling, finite element analysis, modelling interstate conflict, and missing data estimation.
What is blockchain?
A blockchain is a shared distributed database or ledger between computer network nodes. A blockchain serves as an electronic database for storing data in digital form. In a blockchain, data is gathered in groups called blocks that each include data sets. Blocks have specific storage capabilities, and when filled, they are sealed and connected to the block that came before them to create the data chain known as the blockchain. Every additional piece of information that comes after that newly added block links to a brand-new block, which the connects to the chain once it is full. The innovation of a blockchain is that it fosters confidence without the necessity for a reliable third party by ensuring the fidelity and security of a data record.
Integration of blockchain with AI
Now that you have a basic understanding of blockchain and AI, it is safe to proceed to the challenges in blockchain technology addressed by AI. AI offers several solutions to the issues in blockchain, including energy consumption, data storage, security, privacy, etc. The figure below summarizes the issues:
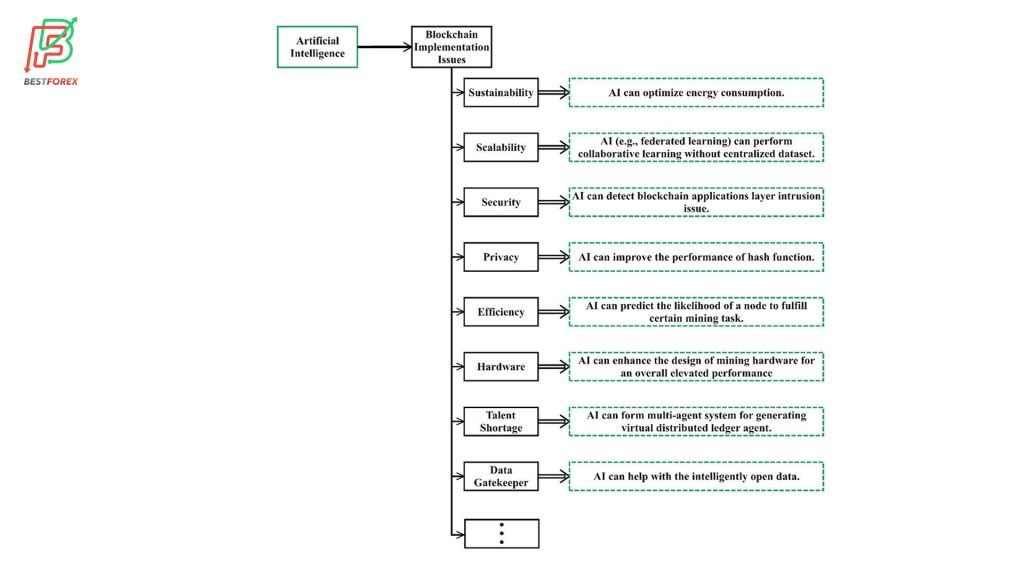
Sustainability
Long before the advent of computers, large-scale systems (such as the design and operation of power systems) were optimized using AI approaches. Furthermore, intelligent optimization algorithms are the fundamental instruments for analyzing the microeconomic environment. In essence, both microeconomics and blockchain (or distributed ledger systems) are large-scale distributed systems, and we can make connections between them.
A microeconomic system, which includes a social system made up of producers, consumers, and markets, and a blockchain system, which consists of a variety of nodes, including full nodes, mining nodes, and lightweight nodes, have many similarities in terms of their interconnected subsystems, decentralized computations, and other features. Microeconomics’ primary focus is distributing limited resources among different applications to maximize producers’ profit and users’ utility. Therefore, a unified vision of AI-backed blockchain system energy consumption optimization can form from the standpoint of large-scale complex systems.
Scalability
In the context of blockchain, scalability often refers to how the network can handle the traffic as the number of transactions increases on the blockchain. In reality, there are many ways to look at scalability challenges, including latency (the amount of time needed to confirm a transaction), bootstrap time (the amount of time required to validate a transaction), and the cost of completed transactions. these scaling problems generally limit the effectiveness of a blockchain system. Additionally, the volume of transaction data contained in each block makes it difficult for traditional centralized data mining approaches to handle the problem. However, cutting-edge AI algorithms, like federated learning, may absorb knowledge from diverse data sources, providing an ideal worldwide solution for the intended blockchain system.
Security
A blockchain system’s security issues include data encryption technology and application layer vulnerabilities (such as those in smart contracts). The Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and Intrusion Protection System (IPS) are essential elements for monitoring various threats concerning the vulnerability of the applications layer.
Developers have frequently used Swarm intelligence, a branch of AI that draws inspiration from swarms of various biological systems, to boost an IDS’s effectiveness. Computational intelligence, another essential subfield of artificial intelligence, is crucial to both traditional and contemporary cryptographic systems, including the blockchain data encryption process. Their uses in this area include hash function (artificial neural network), cryptanalysis (evolutionary computation), and cryptography (e.g., cellular automata and DNA computing). In general, the benefits of applying computational intelligence include building more resilient security protocols and enhancing the robustness of blockchain systems through improved system attack-defense mechanisms.
Privacy
As blockchain systems incorporate more personal information, data encryption emerges as a critical concern for ensuring users’ privacy. This factor concerns a previous security concern in which we highlighted the significant contribution of AI. Consider the blockchain-based Bitcoin system, which currently generates private and public keys based on elliptic curves. But as of yet, no one has succeeded in creating a fault-tolerant public-key algorithm. The bits of a secret key can be searched using a variety of intelligent search algorithms in combination, which would involve a thorough study and exploitation of the search space.
Efficiency
Simply boosting the network’s overall throughput may not always be enough to maintain the necessary transaction validation process. For example, in a sensor network, when used to track the movement of specific items over a vast observation area, the total throughput maximization technique may not be fair to all mining nodes, i.e., the majority of nodes cannot participate in the process due to the high cost of data transfer.
Network Utility Maximization (NUM) is an AI-based solution to congestion, routing, and scheduling in computer networks (including the Internet and the nascent blockchain network). NUM is essentially a differentiable utility function with concavity and non-decreasing characteristics that measure the network’s available resources. Therefore, AI can undertake active and dynamic learning to hasten resource estimation and enhance system performance as a whole.
Hardware
Shenzhen, China, plays a crucial role in maintaining blockchain systems using specialized computer components. Von Neumann’s architecture is the foundation of modern computer architecture, which divides a computer into various parts like internal memory, external storage, input/output (I/O) devices, Central Processor Unit (CPU), and buses (the wires that link these parts together). Other computer architectures incorporate parallelism, RISC (reduced instruction set computers), and Harvard architecture. Regarding the use of AI in hardware development, neural-inspired neuromorphic hardware sheds light on a new course. One instance of such hardware is the synaptic phase change memory cells and neurons, which follow the spiking neurons model with leaky integrate-and-fire and spike-timing-dependent plasticity.
Talent shortage
One option, given the current shortage of blockchain workers, is to use a multi-agent method. The process of writing/reading transaction data from blocks can thus be totally automatic through constructing various task-oriented virtual agents. In addition, artificial intelligence-assisted online learning can also support us in developing critical blockchain skills.
Data gatekeeper
Given the widespread adoption of the data economy, intelligent, open data storage is a primary priority. In addition, companies and individuals require assistance with the data at hand about their accessibility, use, and sense-making as data resources built on blockchain technology become more and more readily available. The capabilities of AI can solve such tasks.
Final words
Artificial intelligence is becoming part of our daily life, but it has other use cases in other technological domains, such as blockchain. Blockchain is a relatively new technology, and its development has several challenges. This article addresses the issues and explained how Artificial Intelligence can contribute to overcoming these challenges.
Source: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1802.04451
Read more articles here.






















Greetings! Very useful advice in this particular article! Its the little changes that will make the biggest changes. Thanks for sharing!